В аннотации написано, что полоцкое княжество подчинялось монархам русским, чьи отпрыски правили в южной Руси. литовцами с чьимт русскими волостями правил Ягайло.
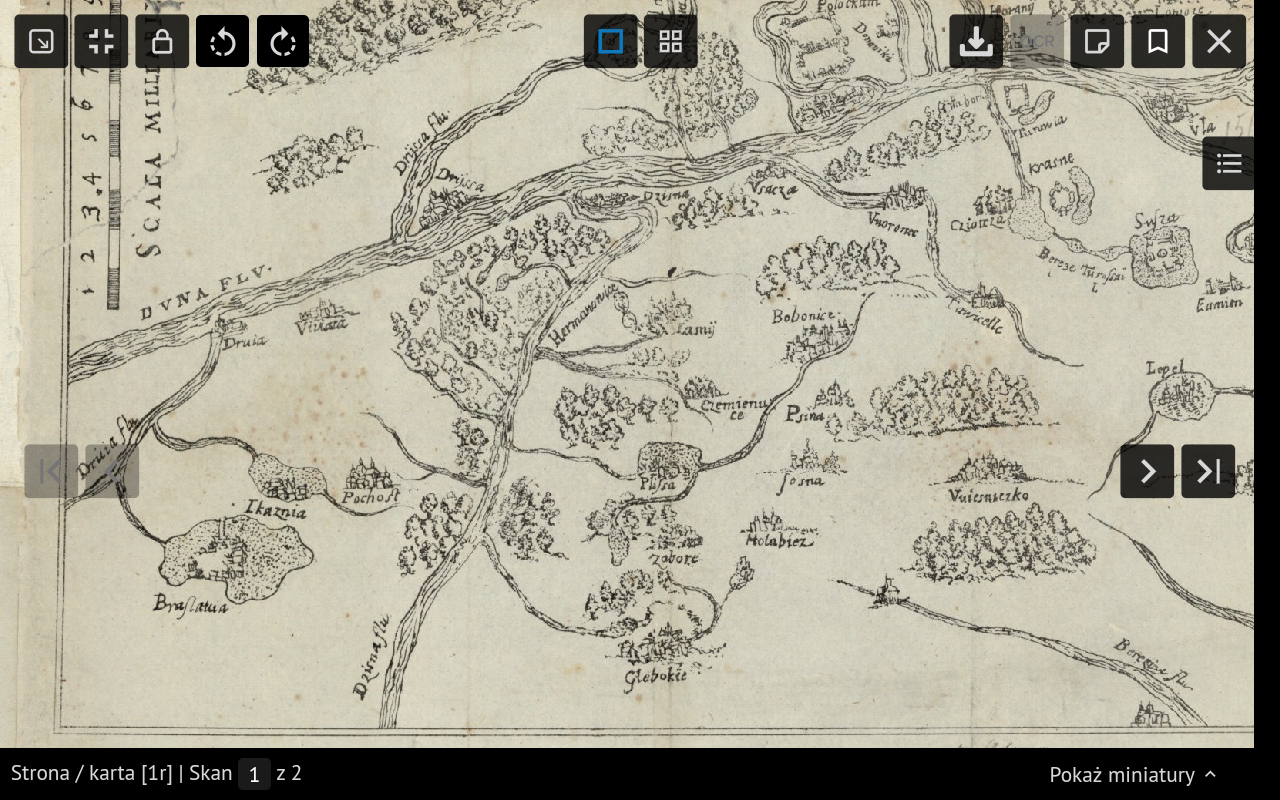
Polotia priscis temporibus ſub annum ſcilicet Christi 980, uel ut Ruſsi ſupputant á | creato mundo 6488. ſuú peculiarem Ducem habuit Rochuoldú Qui á Wlodimirio magno | ob negatá in matrimoniú fi liam Rochnedam, (ut annales Moſcorú perhibent) bello uictus | uitam pariter cú duobus fi lijs ac imperio amisit. Inde Monarchis Ruſsiæ paruit, quorú ſub= | lata ſt irpe ea quæ in Anſtrali Ruſsia regnabat, Lituanis cum quibusdam ditionibus Ruſsicis | conceſsit. Iagiellone apud Lituànos primú, inde apud Polonos regnante Andreas fŕ. ipsius | Polotiæ dńatú arripuerat, ferè cú ipse Iagello Cracouiæ Coronaretur ſed mox missis copijs | cú arce inptēm regis uenit, inde eius dominatus a Magnis Lituaniæ Ducibus et Regibus | Poloniæ continuatus eſt ad annū is63. Quo a Ioanne Baſi lij.F.Duce Moſcouiæ capta eſt eiusq3 | ditionis ager aliquot nouis excitatis arcibus fi rmatus. Nunc uero demú anno is79 et ipsa | Polotia et arces reliquæ per Seren: Polon: Regé Stephanú partim captæ partim deletæ | uniuerſusq3 ille Ducatus receptus. Ditio hæc ad 30 milliaria in longitudiné in latitudiné uix minus | patet, ac propter ubertaté glebæ ac fl uminú aliquot, imprimis uero Dunæ omnium prope Europæ fl u= | uioϗ pulcherrimi amoenissimi et ad nauigandú accomódatiſsimi opportunitaté Rigenſi sq3 portus propinqui= | tatè, ϝ Polotia dú à Mosco caperetur diuitijs incolaϗ ipsam Vilnam ſuperabat. Regius præfectus Poloce= | nsis cú ordine Senatorio Palatini titulum et dignitatem habet. ϝ abundantiſsima (to słowo zostało zapomniane przez rytownika w przedostatnim wierszu)
https://ejournals.eu/czasopismo/terminus/artykul/ryciny-prezentujace-kampanie-polocka-1579-r-jako-jednolita-kompozycja-kartograficzna
Kazimierz Kozica Zamek Królewski w Warszawie – Muzeum k.kozica@zamek-krolewski.pl Charakterystyka prac kartografi cznych Stanisława Pachołowieckiego (1580)
http://elib.shpl.ru/ru/nodes/16093-vyp-2-1912#mode/inspect/page/339/zoom/4
Перевод аннотации к карте, выполненный искусственным интеллектом(Chat GPT)
Polotia in ancient times, around the year 980 AD, or as the Russians calculate, from the creation of the world 6488, had its own unique Duke, Rochuold. He was defeated in battle by Vladimir the Great because he refused to give his daughter Rogneda in marriage (as the annals of the Muscovites report), and he lost his life along with his two sons and his principality.
After this, Polotia submitted to the Russian monarchs, among whom were certain regions that were ruled in Southern Russia, and the Lithuanians, with certain Russian territories, were granted. Under the rule of Jogaila in Lithuania and later under the reign of King Andrew of Poland, who had taken possession of Polotia's lands, it was nearly entirely controlled by Jogaila when he was crowned in Kraków. However, shortly after this, with military assistance and the capture of a fortress, the king's authority was restored. From there, his dominion continued under the great Dukes of Lithuania and Polish Kings until the year 1563.
Later, it was captured by Ivan the Terrible, Grand Duke of Moscow, who strengthened the region with several newly constructed fortresses. However, in 1579, Polotia and the remaining fortresses were partly captured and partly destroyed by the Serene King of Poland, Stephen, and the entire Duchy was retaken.
This region extends about 30 miles in length and scarcely less in width, and because of the fertility of its land and several rivers, especially the Daugava (one of the most beautiful and navigable rivers in Europe), along with its proximity to the port of Riga, Polotia, once taken by Moscow, surpassed even Vilna (Vilnius) in wealth.
The royal prefect of Polotia holds the title and dignity of a Palatine within the Senate.
Полотия в древние времена, около 980 года нашей эры, или, как считают русские, от сотворения мира 6488, имела своего уникального князя, Рохольда. Он был побежден в битве Владимиром Великим, потому что отказался взять в жены дочь Владимира, Рохнеду (как сообщают летописи московитов). В результате он потерял свою жизнь, двух дочерей и империю.
После этого Полотия подчинялась русским монархам, среди которых были территории, которые находились под управлением в Южной Руси, а литовцам с некоторыми русскими землями были предоставлены права. Под правлением Ягайло в Литве, а затем под властью польского короля Андрея, который завоевал земли Полотии, она почти полностью попала под контроль Ягайло, когда он был коронован в Кракове. Однако вскоре после этого, с военной поддержкой и захватом крепости, власть короля была восстановлена. С этого момента его власть продолжалась под великими князьями Литвы и польскими королями до 1463 года.
Позже Полотия была захвачена Иваном Грозным, великим князем Московским, который укрепил регион несколькими новыми построенными крепостями. Однако в 1579 году Полотия и оставшиеся крепости были частично захвачены и частично разрушены Серенейшим королем Польши Стефаном, и вся княжеская область была снова захвачена.
Этот регион простирается на 30 миль в длину и почти на такую же ширину, а благодаря плодородию земли и нескольким рекам, особенно Даугаве (одной из самых красивых и судоходных рек Европы), а также близости к порту Рига, Полотия, однажды захваченная Москвой, превосходила даже Вильну (Вильнюс) по богатству.
Королевский префект Полотии носит титул и достоинство палатина в Сенате.
Rastawiecki, Edward (1805-1874)
Mappografia dawnej Polski, 1846, s. 123
https://polona.pl/preview/9f25e472-01f6-4f4d-af07-583b6f0df967
Дополнено 20.10.2025 от пользователя телеграм Шушпинчик
De bello Moscovitico commentariorum, Рейнгольд Гейденштейн, Краков, 1584 г.
Книга 2.
// В древности Полотск имел своих князей и, около 988 года от Р. Х. или по Русскому исчислению — 6488 от сотворения мира, подчинялся князю Рогволоду, который, как повествуют Московские летописи, за отказ выдать замуж свою дочь Рогнеду, был подвергнут нападению Владимиром Великим и, вместе с двумя сыновьями, потерял жизнь и власть. С того времени он перешёл во владение монархов и князей Русского народа, и когда правивший в Южной Руси род угас, он перешёл к Литве, как и некоторые другие Русские владения.











Комментариев нет:
Отправить комментарий